Research-Based Game Design for Serious Games

It is very easy to gamify or incorporate games (virtual or otherwise) into a lesson plan to improve learning and/or motivate learners to be engaged. How can we ensure that they not only improve learning but cause learning as well?
Motivation Matters: Three Motivation Strategies to Support Engagement in Mathematics
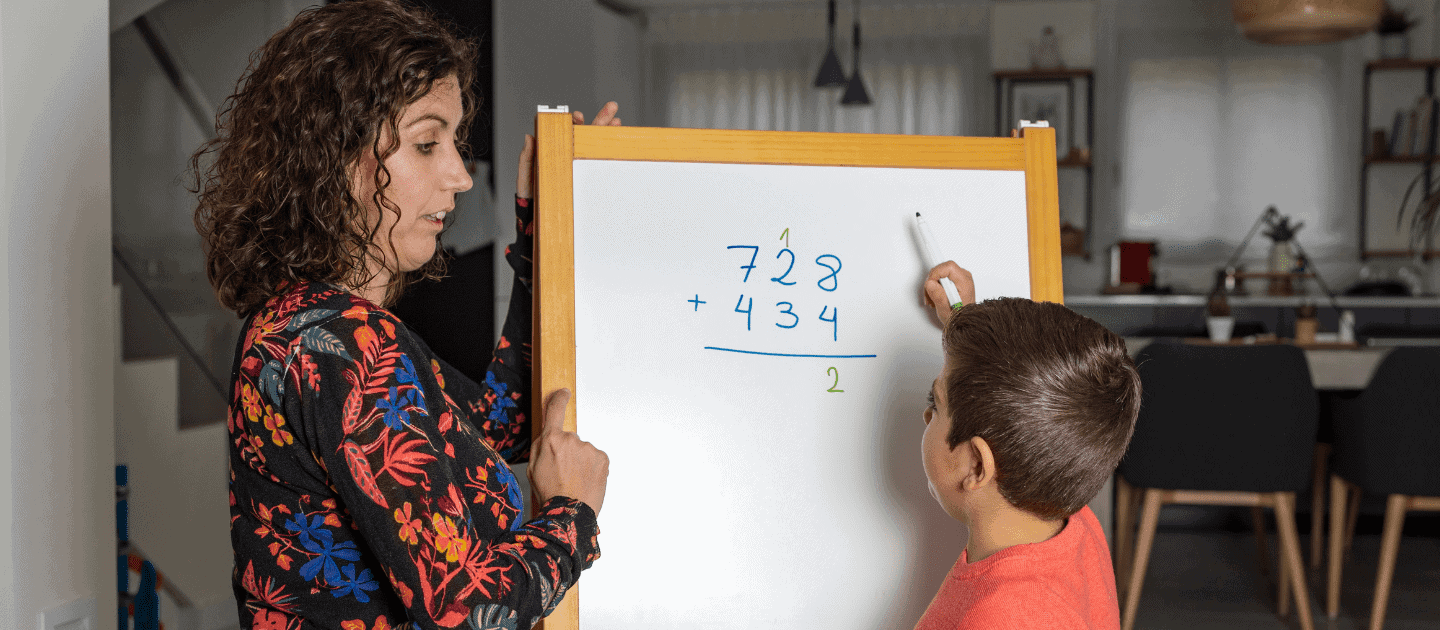
Elementary students with or at risk of emotional and behavioral disorders (EBD) often experience failure and frustration in mathematics. With high-quality instruction and motivation strategies, such as reinforcing engagement, self-monitoring strategies, and using the high-p strategy, we can improve student engagement and motivation to scaffold learning.
The Ineffective Support of a False Growth Mindset

Improving our understanding of the mindsets of students with learning disabilities (LD) will permit the implementation of meaningful supports.
The Use of Virtual Learning Environments to Support Identity-Based Motivation

It is important to establish that difficulties are part of learning and that disfluency can open up possibilities for identity exploration. Virtual learning environments (VLEs) can be designed in such a way that they support this exploration, by looking at features such as gamification, engagement and connection, and learning supports.
How important is specialized professional development?

Effective PD should be sustained over time, involve coaching or collaborative communities, and include specialized and role-specific content.
Teaching & Learning in the Online Classroom: Reimagining Pedagogy to Engage Our Learners

Moving towards learner-centered instruction, well-designed online teaching should encourage students to remain motivated and engaged by providing diverse, collaborative learning activities and creating a space where students are empowered to take control over their own learning.
Academic Self-Concept and Self-Perceived Inclusion in Relation to Student Characteristics

DeVries, Knickenberg, and Trygger report complex relationships between student characteristics (ie. the presence of learning differences), and self-perceived inclusion and academic self-regard.
The personal and external factors needed for students with disabilities to be successful at university

Identifying these internal and external factors can help universities ensure that they have the necessary resources in place to support students with disabilities.
How do temperament and character play a role in students’ approach to learning?

Students with a deep approach to learning tend to have character traits associated with openness, conscientiousness, and a “steady temperament.”
Addressing Overrepresentation of English Language Learners in Special Education during the COVID-19 Pandemic

Implementing six effective vocabulary acquisition strategies (VAS) within the frameworks of self-regulated and multimedia learning may not only have promising effects on the language acquisition of ELLs but it may also prevent ELLs being falsely identified for special education eligibility.
